Demystifying the Blockchain: A Comprehensive Look at the Technology of the Future
Demystifying the Blockchain: A Comprehensive Look at the Technology of the Future
The digital age has ushered in a new era of innovation, and at the forefront of this revolution stands blockchain technology. Often associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain offers a powerful and secure way to record and track information, with the potential to transform numerous industries beyond just finance.
In this article, we delve deep into the world of blockchain, exploring its core concepts, functionalities, and potential applications.
Unpacking the Basics: Understanding Blockchains
Imagine a shared digital ledger, accessible to everyone, where transactions are recorded transparently and immutably. This is the essence of blockchain technology. It functions as a distributed ledger, meaning the data is not stored in a single location but replicated across a network of computers called nodes. These nodes act as independent validators, ensuring the security and integrity of the network.
Building the Chain: How Blocks Work
The core unit of information on a blockchain is a block. Each block holds a specific amount of data, along with important details such as:
- Timestamps: Recording the exact time and date of the transaction.
- Cryptographic Hash: A unique digital fingerprint that identifies the block and links it to the previous one, forming a chain.
- Transaction Data: The actual information being recorded, such as financial transactions, ownership transfers, or any other relevant data.
The Power of Immutability: Guaranteeing Security
One of the most crucial features of blockchain is its immutability. Once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This is achieved through a combination of cryptographic techniques:
- Hashing: Each block’s data is converted into a unique code (its hash) using a mathematical function. Any change to the data would result in a completely different hash, making it impossible to modify a block without altering the entire chain.
- Proof of Work (PoW): In this consensus mechanism, miners (nodes on the network) compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate a block and add it to the chain. This process requires significant computing power, making it extremely difficult to tamper with existing blocks or add fraudulent data.
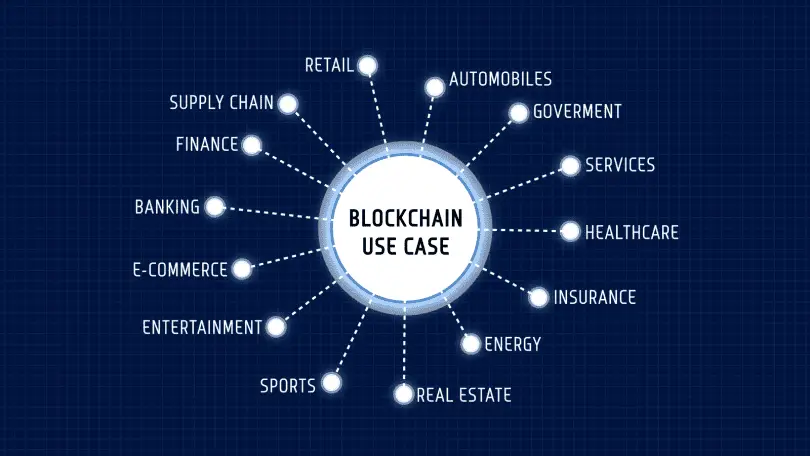
Beyond Crypto: Exploring the Diverse Applications of Blockchain
While cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum brought blockchain into the spotlight, its potential extends far beyond the financial realm. Here are just a few areas where blockchain is making waves:
1. Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the movement of goods and materials through the supply chain, ensuring transparency, traceability, and efficiency. This allows businesses to monitor product quality, prevent counterfeiting, and optimize logistics.
2. Secure Voting Systems: Blockchain-based voting systems can enhance the security and transparency of elections by creating an immutable record of votes and reducing the risk of fraud.
3. Healthcare Data Management: By leveraging blockchain, patients can gain greater control over their medical records, ensuring secure and accessible data storage. This can also enable seamless data sharing between healthcare providers, improving patient care coordination.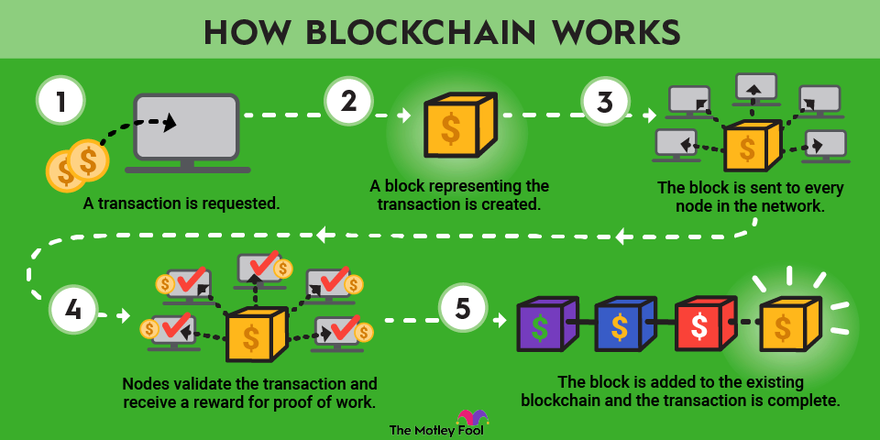
4. Intellectual Property Protection: Blockchain can help secure intellectual property rights such as patents, copyrights, and trademarks. The immutable nature of the blockchain provides a clear record of ownership and can deter unauthorized use.
5. Identity Management: Blockchain-based identity systems can offer individuals a secure and portable digital identity. This can streamline various processes, from opening bank accounts to voting, and reduce the risk of identity theft.
Navigating the Challenges: Looking Ahead
Despite its immense potential, blockchain technology is still in its nascent stages of development. Several challenges need to be addressed before it can reach its full potential:
- Scalability: Existing blockchain networks often struggle to handle large volumes of transactions, which can limit their adoption in certain domains.
- Regulation: The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain is still evolving, which can pose uncertainties for businesses looking to leverage this technology.
- Energy Consumption: Some consensus mechanisms, like Proof of Work, require significant computing power, raising concerns about the environmental impact of these systems.
Unveiling the Advantages of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, often associated with its role in cryptocurrencies, boasts a remarkable array of benefits that extend far beyond finance. Its innovative approach to data management presents several significant advantages over traditional methods, paving the way for a more secure, transparent, and efficient future.
1. Enhanced Security and Immutability:
- Tamper-proof data: Blockchain’s core principle of immutability guarantees that once information is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This cryptographic feat, achieved through hashing and consensus mechanisms, creates a highly secure environment resistant to fraud and data manipulation.
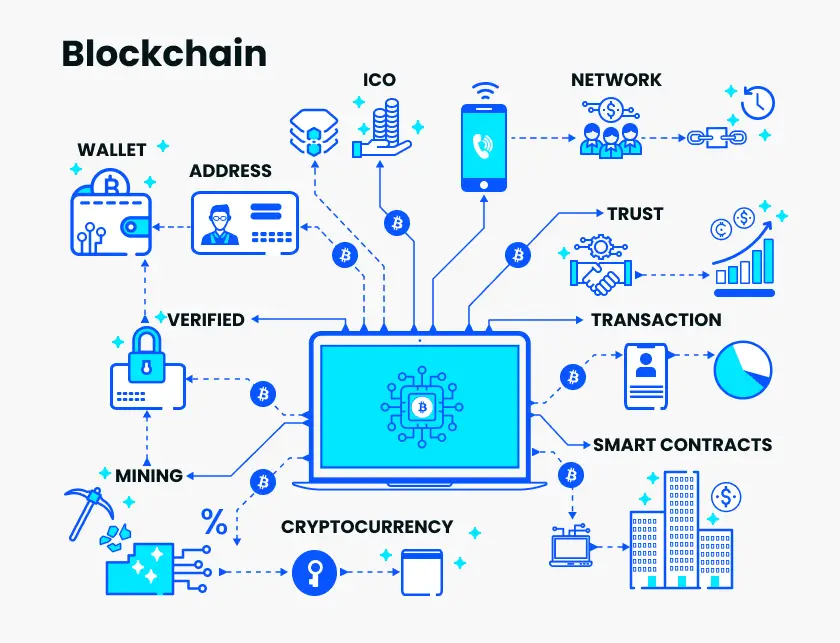
2. Increased Transparency and Trust:
- Distributed ledger: All participants in a blockchain network have access to the same shared ledger, fostering transparency and traceability. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, allowing all parties to verify transactions and data accuracy independently, leading to increased trust within the system.
3. Improved Efficiency and Automation:
- Streamlined processes: By automating tasks and eliminating the need for reconciliation processes, blockchain can significantly improve efficiency. This translates to faster transaction processing, reduced operational costs, and increased productivity across various industries.
4. Reduced Costs and Eliminating Intermediaries:
- Decentralized nature: Removing the need for central authorities reduces administrative costs and streamlines transactions. This decentralized approach also empowers individuals and organizations by giving them greater control over their data and assets.
5. Enhanced Traceability and Supply Chain Management:
- Real-time tracking: Blockchain allows for the real-time tracking of goods and materials throughout the supply chain. This provides greater visibility and transparency into every stage of the process, facilitating efficient logistics, improving quality control, and preventing counterfeiting.

6. Secure and Convenient Identity Management:
- Portable digital identity: Blockchain technology can revolutionize identity management by offering individuals a secure and portable digital identity. This allows for seamless verification across various services and online platforms while minimizing the risk of identity theft and fraud.
7. New Opportunities and Innovation:
- Unlocking potential: The flexibility and security of blockchain open doors to new business models and innovative solutions across various sectors. Its potential applications are vast, ranging from secure voting systems and healthcare data management to intellectual property protection and efficient energy trading.
Conclusion: A Promising Future for Blockchain
While still in its early stages, blockchain technology has already captured the imagination of individuals and organizations across the globe. Its unique features offer a compelling alternative to traditional methods by providing unparalleled security, transparency, and efficiency. With ongoing advancements addressing scalability, regulatory frameworks, and energy consumption concerns, we can expect wider adoption and groundbreaking applications emerging across various sectors. From transforming supply chain management to securing identities and enabling new forms of digital interaction, the future of blockchain is brimming with possibilities. As we navigate this exciting technological frontier, it is crucial to foster collaboration, explore ethical considerations, and prioritize innovation, ensuring that the benefits of blockchain technology are harnessed for the betterment of society.